Understanding the term “Blood pressure”
Blood pressure is the pressure of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries. Arteries carry blood from the heart to other parts of your body.
Blood pressure normally rises and falls throughout the day, but it can damage the heart and cause health problems if it stays high for a long time.
Blood pressure is measured using two numbers: Systolic and Diastolic
The first number, called systolic blood pressure, measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats.
The second number, called diastolic blood pressure, measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats.
Normal Blood Pressure is 120/80 mmHg
Hypertension is persistently high arterial blood pressure, defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 140mm Hg or higher or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) 90mm Hg or higher.
Ideal method of blood pressure measurement and diagnosis of Hypertension
Blood pressure should be measured with a well calibrated sphygmomanometer. The cuff should encircle at least 80% of the arm circumference. Reading should be taken after the patient has been resting comfortably for at least 5 minutes and at least 30 minutes after smoking or coffee ingestion.
Important facts about Blood pressure
- A high waist circumference and high body mass index (BMI) increases your chances of having high blood pressure, high cholesterol and high blood sugar.
- Blood pressure is normally lowest at night and the loss of this night-time dip is strongly associated with cardiovascular risk, particularly stroke.
- An increase in the normal morning blood pressure is associated with increased likelihood of brain hemorrhage.
- In winters the blood pressure rises in comparison to summers, so it is advisable to get your medication & dietary intake adjustments done accordingly.
- 1 kg increase in body weight, increases risk of Hypertension by 5% as was evident in a large study conducted on women.
- Another study found that hypertension is about twice as prevalent in the obese than the non-obese of both sexes.
- Weight loss in the range of 2 to 4 kg is associated with systolic blood pressure decline, in the range of 3 to 8 mm Hg, a clinically significant impact.
Cause of High blood pressure
- In 95 % of patients, no cause for hypertension can be identified. Usually genetic or/and environmental factors play a role.
- Approximately 5% of patients have an identifiable cause such as Diabetes, Obesity, chronic kidney diseases, sleep apnea, drug induced, thyroid diseases, associated with pregnancy, renal vascular problem.
Risk factors for developing Hypertension
A number of conditions elevate blood pressure, especially in predisposed individuals.
- Obesity
- Unhealthy Diet and excessive salt consumption
- Low potassium intake
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- Alcohol intake
- Tobacco use
- Stress
- Genetics and family history
Symptoms of hypertension
Hypertension is called a “silent killer” because for years blood pressure can be asymptomatic (i.e. no symptoms) till it suddenly causes organ damage. This damage can lead to visual disturbances, palpitations, angina, headaches, transient weakness in various body parts, breathlessness, swelling in face and/or feet or general fatigue.
Importance of getting blood pressure tested
High blood pressure usually causes no symptoms. Therefore, everyone should have regular blood pressure checks, at least every 3-5 years. The check should be more often (at least twice a year) in older people, people who have had a previous high reading and people with diabetes.
Alert 1 : If you have a family history of Hypertension, keep an eye on your Blood Pressure.
Alert 2 : If you have had a history of Gestational Diabetes, keep regular check up on your Blood Pressure.
If you are diagnosed as having high blood pressure then you are likely to be examined by your doctor and have some routine tests which include:
- A urine test to check if you have protein or blood in your urine
- A blood test to check that your kidneys are working fine and to check your cholesterol and sugar level.
- A heart tracing (an electrocardiogram, also called ECG).
- Eye check & fundus examination.
- Echocardiogram.
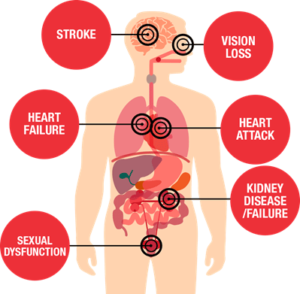
Know the complications of high blood pressure
Over a period of time high blood pressure can cause problems in other parts of the body because of the damage to the blood vessels. These include
- Stroke
- Angina, myocardial infarction
- Missed or extra heart beat
- Heart failure
- Carotid artery blockage
- Weakening of artery wall that creates a bulge, or distention of the artery
- Peripheral artery blockage in lower limbs
- Visual impairment
- Renal impairment
Tips to manage Hypertension
If your blood pressure is too high, you can make healthy changes to your lifestyle to help bring it down. The following changes to your lifestyle can have a real effect on your blood pressure.
Maintain a healthy weight – Losing weight, if you need to, will help lower your blood pressure and reduce your risk of health problems. The best way to lose weight is to reduce your calorie intake and increase physical activity. Reduce your calorie intake by avoiding foods that contain a lot of added sugar and fat, such as colas, sweet drinks, fruit juices, cakes, biscuits, fried foods, namkeens etc. Make small changes in your diet and activity levels that you can keep for life.
Eat less salt – Most of the salt you eat is not only the one added while cooking food, but also in prepared foods like bread, breakfast cereals and ready meals. Don’t add salt to food when at the table like curd, salad etc. When shopping for food, check the labels and choose low-salt options when you can.
Eat more fruits and vegetables – to lower your blood pressure. Eat at least five portions of fruit and vegetables every day. Try to eat a range of different seasonal fruits and vegetables.
Get more active – 30 minutes of moderate exercise five times a week can keep your heart healthy, and can lower your blood pressure.
Drink less alcohol
Keep stress under control- Practice relaxation techniques, meditation, breathing exercises and develop time management skills to overcome daily stress.
Take your medicines regularly
Monitor your blood pressure regularly
Go ahead, aim for a normal blood pressure, work towards it and reap the health benefits….



